Sudewo Pati Regent Case Under Media Spotlight: Communication Analysis, Framing, and Public Perception
In recent times, public attention has again turned to leadership dynamics at the local level. Various cases involving regional heads—such…
The government has begun outlining the direction of the 2026 State Budget (APBN 2026) amid ongoing global economic uncertainty. Finance Minister Purbaya Yudhi Sadewa stated that the government is relying on policy synergy between fiscal instruments, the financial sector, and investment as the main engines to sustain economic growth momentum while strengthening Indonesia’s fiscal foundations.
At this point, APBN 2026 becomes highly relevant for deeper examination. It does not emerge in a vacuum, but is formulated amid global pressures, continuing development agendas, and strong public expectations regarding the state’s role. APBN 2026 is positioned as an instrument to maintain economic stability while ensuring the sustainability of national development.
So far, APBN 2026 has often been perceived as a highly technical document filled with numbers, tables, and fiscal terminology. In practice, however, the state budget goes far beyond an administrative function. It serves as a marker of development direction and a space where interests between the state, the market, and society intersect—reflected in the national financial policy framework and reports from international institutions such as the World Bank.
As discussions on the APBN 2026 Bill begin, public attention has intensified once again. Amid global economic uncertainty, geopolitical dynamics, and ongoing development priorities, APBN 2026 is widely seen as a crucial instrument for safeguarding stability while driving growth. It is therefore unsurprising that the issue quickly became a focal point in media coverage and public discourse.
At this stage, the state budget no longer exists solely as government policy, but also as a narrative—framed, debated, and interpreted through media reporting.
From a policy perspective, APBN 2026 occupies a strategic position. The government views this period as a phase of fiscal consolidation following major development programs and economic recovery efforts. Finance Minister Purbaya Yudhi Sadewa emphasized that the government is banking on synergy between fiscal policy, the financial sector, and investment to drive economic growth, while maintaining fiscal discipline and sustainability.
The government faces the challenge of balancing budget discipline with public spending needs, ranging from social protection and infrastructure development to strengthening productive sectors.
External pressures such as global economic slowdown and commodity price fluctuations also affect fiscal space. At the same time, public expectations of the state’s role remain high. APBN 2026 is thus formulated amid limited fiscal room, while still being required to respond to public needs.
For the public, the state budget is not merely a national financial plan. It directly affects the prices of basic goods, energy subsidies, job creation, and the quality of public services. As a result, discussions around the APBN almost always generate widespread responses.
Public attention to APBN 2026 is inseparable from its tangible impact. Issues such as subsidy levels, budget deficits, and the effectiveness of state spending are among the most frequently highlighted topics. At this stage, the role of the media becomes crucial.
The media not only delivers information, but also shapes how the public understands policy. The choice of perspective, emphasis on certain issues, and the language used in reporting all contribute to the formation of public perception. The same APBN can appear either as a symbol of development optimism or, conversely, as a source of fiscal concern.
As the bridge between state policy and public understanding, the media plays a major role in framing APBN 2026. Complex fiscal policies are translated into narratives that are more accessible to the public, though simplification is sometimes unavoidable.
To objectively identify these patterns, data-driven analysis is needed so that public understanding does not rely solely on impressions or momentary opinions.
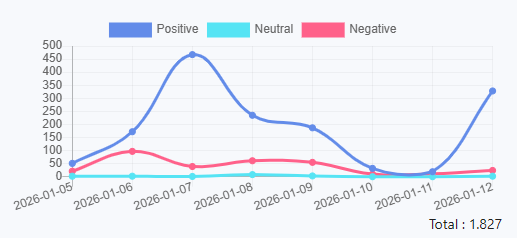
Newstensity analysis shows that media coverage of APBN 2026 is dominated by positive sentiment, particularly in the early stages of discussion. This optimism is generally linked to narratives about development continuity, economic stability, and the role of the state budget in maintaining purchasing power.
Nevertheless, negative sentiment also appears periodically. Issues such as potential budget deficits, spending effectiveness, and long-term fiscal burdens are the main drivers of critical coverage. This pattern indicates that media narratives are not uniform, but instead present a diverse spectrum of perspectives.
Beyond sentiment, word choices in media reporting also reflect how APBN 2026 is framed.

Picture 2. Word cloud of APBN 2026 media coverage based on word frequency. (Source: Newstensity)
The word cloud shows that terms such as APBN, government budget, deficit, spending, and economic recovery dominate coverage. This suggests that the media tends to highlight APBN from the perspective of fiscal stability and the state’s capacity to finance development.
Meanwhile, more technical discussions on budget structure or long-term fiscal risks receive relatively less attention. This pattern illustrates how media outlets select aspects most relevant to public interest, while potentially simplifying the complexity of fiscal policy.
Amid the rapid flow of information, data-driven approaches are becoming increasingly important. Media intelligence allows public issues to be examined more comprehensively—not just through one or two articles, but across the entire media landscape.
Through analyses such as those conducted by Newstensity, the dynamics of the APBN 2026 issue can be mapped systematically: when media attention peaks, which topics dominate, and how sentiment shifts over time. This approach helps both the public and policymakers understand the broader context behind circulating narratives.
Ultimately, APBN 2026 is not only about numbers in a state document. It lives in the public sphere, shaped by policy decisions, competing interests, and the way the media frames it.
Understanding the APBN as a narrative does not mean ignoring policy substance. On the contrary, it opens space to read policy more holistically—between what is planned, what is reported, and how it is interpreted by the public. In this complexity, data and analysis become essential to ensure that public discourse remains grounded in clear understanding.
In recent times, public attention has again turned to leadership dynamics at the local level. Various cases involving regional heads—such…
A topic went viral on February 21, involving alumni of Indonesia’s Education Endowment Fund (LPDP). Dwi Sasetyaningtyas and her husband,…
Lately, the term SEAblings has been widely discussed across social media. The phenomenon gained traction after tensions between Southeast Asian…
Lieutenant Colonel Teddy Indra Wijaya, the Cabinet Secretary of the Republic of Indonesia, is currently carrying three major roles at…
The government’s decision to appoint personnel from the Nutrition Fulfillment Service Unit (SPPG) as Government Employees with Work Agreements (PPPK),…
The evolution of marketing over the past few years has shown a major shift, especially as digital marketing becomes the…
Freedom of opinion and expression is a constitutional right protected by law. Today, the public’s channel for voicing disappointment toward…
In January 2026, the internet was shaken by the viral spread of a book titled “Broken Strings: Fragments of a…
The Indonesian government, through the Ministry of Communication, Information, and Digital Affairs (Komdigi), has officially temporarily blocked the use of…
A few years ago, electric cars still felt like a far-off future. They were seen as expensive, futuristic in design,…